What is CATIA?
Table of contents
- What is CAD (Computer Aided Design)?
- What is CAE (Computer Aided Engineering)?
- What is CAM (Computer Aided Manufacture)?
- What is the Current Version of CATIA?
- What is CATIA 3DEXPERIENCE?
- Which Functionalities Does CATIA Support?
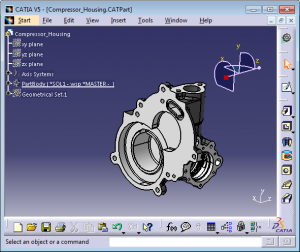
- Part Modelling
- Assembly Modelling
- Surface Modelling
- Finite Element Analysis
- Sheetmetal Part Design
- Rendering
- Engineering Drawing creation
CATIA stands for Computer Aided Three-Dimensional Interactive Application. It’s much more than a CAD (Computer Aided Design) software package. It’s a full software suite which incorporates CAD, CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacture).
So, let’s take a look at each of these areas and the tools that CATIA offers professionals to enhance innovation in product development.
What is CAD (Computer Aided Design)?
Enabling 2D and 3D design
Computer-Aided Design is most employed by Engineers to help create, modify and/or analyze graphical representations of product designs. Its applications stretch across a multitude of industries due to its many popular benefits.
CAD software innovation continues to improve the quality of design through greater accuracy and the reduction of design errors. CAD software is also capable of improving communication due the centralization of design data and documentation, creating a single source of truth for engineers and manufacturers.
What is CAE (Computer Aided Engineering)?
Enabling verification through analysis of 3D models
Computer-aided engineering most used by Engineers for the simulation and analysis of product designs. These analyses commonly include Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and Multibody Dynamics (MBD). Similar to prototyping, these processes help to prepare a product design for real world stresses. This testing enables Engineers to make better product design decisions and revisions – this ultimately leads to better product performance and customer experiences.
What is CAM (Computer Aided Manufacture)?
Enabling manufacturing processes to be designed for 3D model manufacture
Computer-aided manufacturing is commonly used by Manufacturers – rather than Design Engineers – to plan, manage, control and automate manufacturing operations. CAM software uses CAD designs to infer machining instructions while optimizing part production efficiency and material usage.
What is the Current Version of CATIA?
CATIA currently stands at version level 6, better known as CATIA V6.
The first release of CATIA was back in 1977 by Dassault Systèmes, who still maintain and develop the software. It was initially developed for use in designing the Dassault Mirage fighter jet.
Nowadays, the most widely used version is CATIA V5, with CATIA V4 still being used in some industries, mostly in conjunction with V5. Between versions, CATIA has varied significantly in terms of usage and appearance. Each Version brings significant additional functionality. Between V4 and V5, the fundamentals to the design process were developed and between V5 and V6 the handling of data changed. Within each version, Dassault Systèmes also offer updates in the form of releases. New releases are typically released annually and also bring additional functionality within the Version as well as bug fixes.
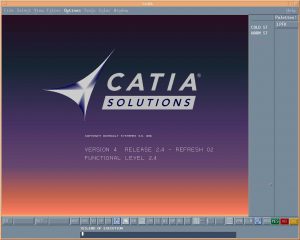
CATIA V4:
CATIA V5:
CATIA V6:
For large organisations, it can be difficult to handle large amounts of data and allow users to share this data. This can be controlled using PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) products. CATIA V5 can be used file based or alongside another software package which incorporates PLM, such as ENOVIA or SMARTEAM. CATIA V6 however already has ENOVIA V6 integrated. The main benefits for using a PLM product are the prevention of data loss and security context control.
What is CATIA 3DEXPERIENCE?
CAD CAM CAE and more on the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform
CATIA 3DEXPERIENCE is essentially the next iteration of CATIA V6. It incorporates Product Data Management (PDM) and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) through ENOVIA with the additional integration of Dassault Systèmes’ other brands such as SIMULIA, DELMIA, and more.
The purpose of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform is to connect other areas of an organization beyond the engineering office. It provides exceptional, web-based PLM as well as the ability to view models without having to install additional applications. Not only does CATIA 3DEXPERIENCE provide a change in Graphical User Interface (GUI), it improves ease of use and an enriched overall experience.
Learn about the major practical differences between CATIA V5 and CATIA 3DEXPERIENCE in our recent webinar.
Which Functionalities Does CATIA Support?
CATIA has capabilities in multiple domains.
The majority of users do not require all functionalities available in CATIA, which has significant cost impacts on the user or organisation. Licenses are therefore broken down to include required functionality and are pre-defined. Depending on the licence, additional workbenches become available and/or additional tools within workbenches become available. Workbenches in CATIA work a bit like different software held within CATIA. They allow the user to perform different tasks, from:
Part Modelling
Part Design workbench
The Part Design workbench enables users to design precise 3D mechanical parts. From assembly sketching to detailed design, the Part Design application accommodates the vast majority of design requirements.
Assembly Modelling
Assembly Design workbench
The Assembly Design workbench enables users to design cooperate with Part Design and Generative Drafting apps on scalable design projects. Various visual tools allow for 3D navigation through large assemblies.
Surface Modelling
Generative Surface Design workbench
the Generative Surface Design workbench enables users to create wireframe construction elements and enrich existing mechanical part design with wireframe and surface features.
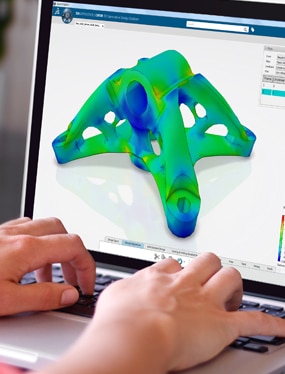
Finite Element Analysis
Generative Structural Analysis
The Generative Structural Analysis enables users to perform first order mechanical analysis for 3D systems.
This workbench includes:
– Generative Part Structural Analysis (GPS) for obtaining mechanical behavior information.
– ELFINI Structural Analysis (EST) for mechanical analysis developments.
– Generative Assembly Structural Analysis (GAS) for analysis of the mechanical behavior of a whole assembly.
– Generative Dynamic Analysis (GDY) for working in a dynamic response context.
Sheetmetal Part Design
Generative Sheetmetal Design
Generative Sheetmetal Design enables users to perform associative feature-based modelling, making it possible to design sheet metal parts in concurrent engineering between the unfolded or folded part representation.
Rendering
Real Time Rendering workbench
The Real Time Rendering workbench enables users to define material specifications that will be shared across the whole product development process, while mapping materials onto parts and products to produce realistic renderings.
Engineering Drawing creation
Generative Drafting workbench
The Generative Drafting workbench enables users to generate drawings from 3D parts and assembly definitions.
Improve productivity with enhanced collaborative engineering, simulation and manufacturing on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.